how to apply K8S HPA(Horizontal Pod Autoscaling)
Outline
HPA refers to the replica expansion of the Pod inside the K8S node. The goal is to designate replication of deployed POD according to CPU usage so that the service can operate smoothly. (This is different from Instance Autoscaling, which increases instances of work nodes to be described later.)Apply sequence (based on AWS EKS)
1. Create a Kubernetes metrics server. Metrics Server aggregates resource usage data across the Kubernetes cluster. Metrics such as CPU and memory usage of a worker node or container are collected through 'kubelet' installed on each worker node.
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/metrics-server/releases/latest/download/components.yaml
If the installation is complete, please check the command below for proper installation
2. Create a replica of the pod that you want to use HPA. Create one of the default values here. Please refer to deployment.yaml belowkubectl get deployment metrics-server -n kube-systemdeployment.yaml --- apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: #[deployment name e.g. demo-flask-backend] namespace: default spec: replicas: 1 #[number of replicas you want] selector: matchLabels: app: #[lable name e.g. demo-flask-backend] template: metadata: labels: app: #[tempalte name e.g. demo-flask-backend] spec: containers: - name: #[container name e.g. demo-flask-backend] image: #[image name which you will deploy ECR] imagePullPolicy: Always ports: - containerPort: #[Pod Port] resources: requests: cpu: 250m limits: cpu: 500m EOF
kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml
3. Create and apply HPA
cat <<EOF> flask-hpa.yaml --- apiVersion: autoscaling/v1 kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler metadata: name: [#Create the name of HPA e.g. demo-flask-backend-hpa] namespace: default spec: scaleTargetRef: apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment name: [# deployment name what you want to use e.g. demo-flask-backend] minReplicas: 1 maxReplicas: 5 targetCPUUtilizationPercentage: 30 EOF
4. Check the Condition
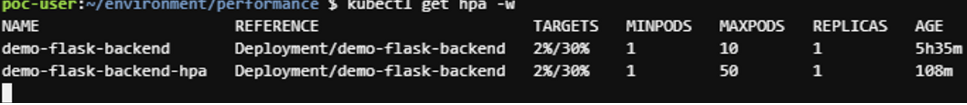
kubectl get hpa -w
If you invoke an application deployed using familiar stress tools such as Apache AD, Locust, and J-Meta, you can see that POD Replica proceeds when the set CPU threshold is exceeded.5. When deletedkubectl delete hpa --all



Comments
Post a Comment